Create a basket composite
Use the enterBasketsComposite mutation to create a basket composite.
A composite can contain different groupings of baskets:
Looped families
#
A Looped Family is a grouping of baskets looped together. This means those baskets must be accepted altogether or not at all. Only baskets of the same unit and on non-overlapping service windows can belong to a looped family.
For the input for the baskets, refer to the Create baskets page. The same logic applies as for the enterBaskets mutation.
Flexible groups
#
A Flexible Group is a grouping of consecutive baskets with a minimum up-time condition. This means that the baskets must be accepted for a minimum number of consecutive service windows or not at all.
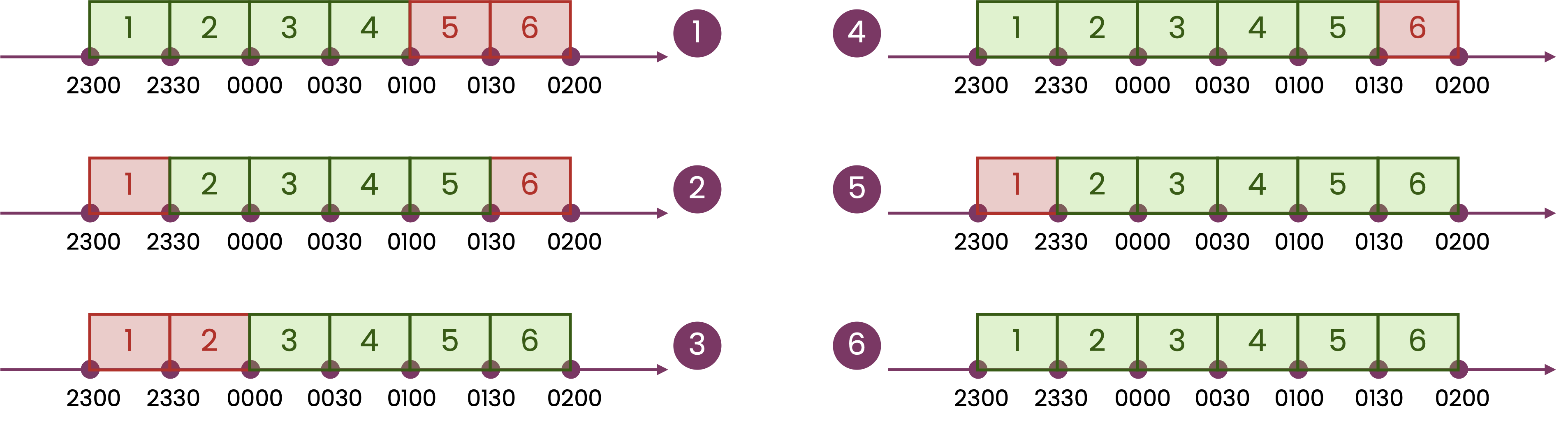
For example, the following inputs request the creation of two flexible groups.
The first one requires that baskets be selected for at least four consecutive service windows. If the group contains six consecutive baskets, any of the following selections would be acceptable:
Baskets of a flexible group must have the exact same structure (parent and child orders) and volumes for all services, but prices can differ.
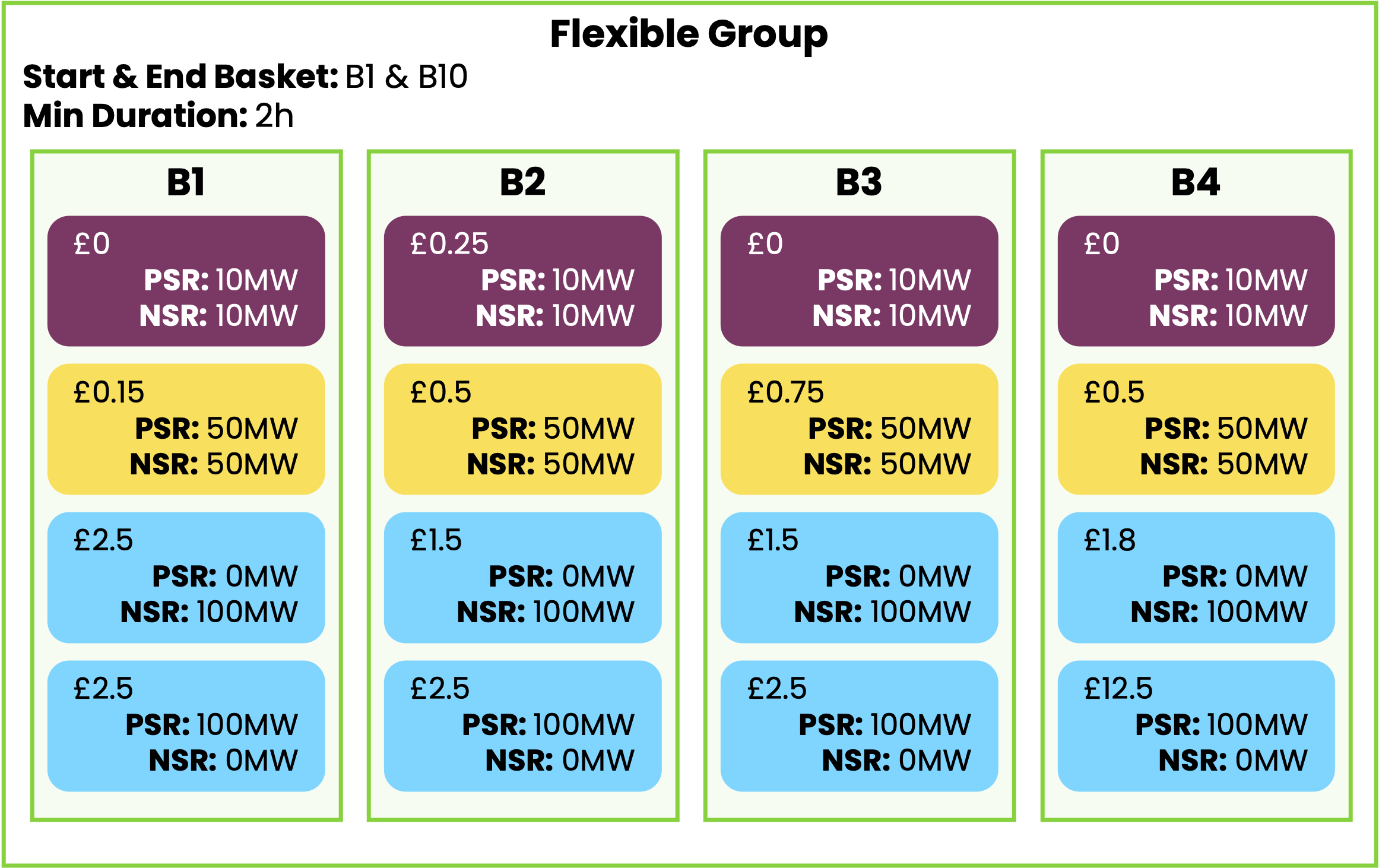
When accepted, baskets will be accepted at a constant volume over the flexible group. Only one consecutive set of baskets can be selected in a flexible group.
For the input for the baskets, refer to the Create baskets page. The same logic applies as for the enterBaskets mutation.
Example
#
All together, it gives us the following query:
Validations
#
The EAC is performing validations to ensure the baskets comply with market rules.
Most of the validation rules are directly explained field by field in the GraphQL reference, see BasketInput for the specifics on basket creation.
The validation rules explained in the Create baskets page apply to the baskets in a composite as well.
Linked service windows
#
If NESO links service windows for a given service, additional validation rules are applied when submitting baskets. Refer to Impact on baskets submission for more information.
Basket composites structure